Tattooing in animals has been a controversial topic for a while now.
We recently had the opportunity to be a part of something very cool.
Little Luna, a very sun and fun-loving pup, was born with no pigment around her right eye. This means that her eye and the surrounding eyelid is super sensitive and create an optimal area for UV rays to wreak havoc.
Her owners opted to have her eyelid, and a small area on her nose, tattooed to protect her from the harmful rays.
We can all agree that melanin and ink are not the same. Melanin is a natural skin pigment that accumulates in the basal layer of the epidermis of the skin. (The deepest most part of the epidermis)
These pigments act as light catchers and serve as direct free-radical scavengers. In the same way, black ink is known to absorb all visible light, and could possibly also absorb UV rays. In this way, it could protect the skin against UV damage. This was studied a few times in horses as well as mice There are also thousands of real-life examples of this phenomenon seen in pets around the globe.
UVA and UVB Rays:
UVA and UVB are main contributors to skin damage when no or reduced pigmentation is seen. Normally pigmented eyelids have melanin-containing cells. Looking at pets, when there is reduced melanin in the skin or eyelid, the UV rays may harm these cells. This results in blood vessels in the deeper skin layers dilate turning the eyelids red and causing intense inflammation and severe irritation and discomfort. When eyelids and other periocular tissues are affected, it’s called solar blepharitis.
Skin Cancer in Pets:
To fully understand what we are trying to achieve by means of tattooing the eyelids or nose, one needs to understand the mechanism of action of skin cancer and, in the case of pets, primarily squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Plainly, the UV rays damage the DNA and in turn disrupts the normal function and patterns of the DNA, causing mutated cells, leading to cancer.
In pets, pre-cancerous cells are actually formed when they are young, and only later evidence of SCC is seen when there has been continued sun exposure.
SCC happens in three stages, the first being the initial irritation/inflammation of the skin. Reducing the intense irritation of the lid and the surrounding structures is what we aim to achieve.
A human example of decreasing “glare” and irritation would be sportsman with black lines under their eyes during sports matches. The “eye black grease” is thought to reduce the glare from the interfering light better than their natural skin tone.
Limiting Sun exposure/Preventing UV Related Complications:
There are very few preventative measures pet owners can take to prevent SCC or related problems when it comes to sun exposure. One being sunscreen, which is very difficult to maintain with pets and another being limiting exposure to the sun. Taking into account that we reside in South Africa, a very sunny country, this means keeping lighter pets indoors for the majority of the day. Sometimes this is just not possible, and the frustration felt by the pet by being cooped up can also serve as a platform for other behavioural issues to take hold. Tattooing of non-pigmented areas that are prone to developing SCC is, at this stage, one of the only more permanent ways veterinarians can assist these pets.
Why We Recommend Tattooing Of Unpigmented Areas In Pets:
It is true that reports from 2010 and 2012 indicated that there is no current definitive evidence to show that the ink itself absorbs or protects against UV damage. The Danish study of 2015 is the most encouraging. It concluded that there is strong indication of the protective effect of black pigment in the dermis attributed to UVR absorption. Thereby reducing backscattered radiation that seems to assist in reducing the extent of skin cancer formation.
Based on this recent knowledge, prophylactic tattooing of the more sensitive areas around the eyes and nose is considered medically beneficial. We acknowledge that no further current research information is available, and we are aware that no known studies have been conducted in dogs and cats. We will constantly be on the lookout for newer research and amend our approach should it be deemed medically significant.
At this stage, the benefits greatly outweigh the risks. If nothing else, reducing the glare and pain associated with the severe irritation of very sensitive eyes and noses is enough reason to condone medical tattooing as veterinary professionals. Therefor it is not considered purely cosmetic.
Disclaimer:
We would like to reiterate again that patients undergoing the procedure will be consulted by our veterinarians. These patients will need to be deemed at high enough risk to warrant tattooing. We do not condone tattooing of animals for purely cosmetic reasons. Kimberley Veterinary Clinic also does not claim that tattooing prevents pets getting cancer.
If you would like a more in detailed explanation, feel free to visit the Johannesburg Animal Eye Hospital website (https://animaleyehospital.co.za/Tattooing/). Most of our own research and facts stem from their own detailed description of the different processes. They are veterinary eye specialists and also advocate for medical tattooing of predisposed pets. They also cite the research articles referenced within their own post.
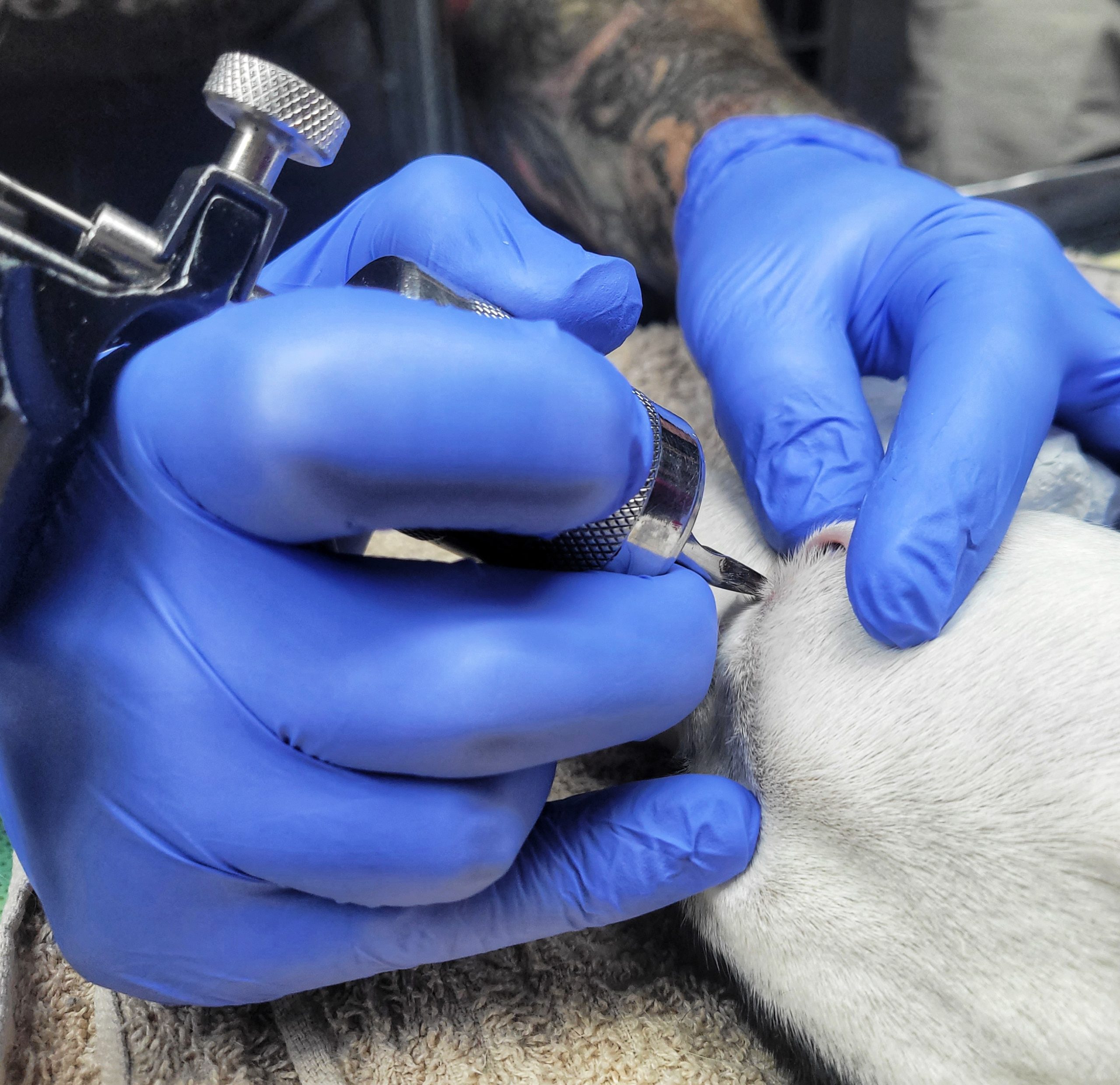
Luna’s Procedure:
Luna’s procedure was done ethically and under highly controlled circumstances and not for cosmetic purposes.|
Leon, from VanCustoms – Tattoo’s and Body Piercings, performed the tattooing procedure. He has extensive experience tattooing humans and pets alike, and the procedure was expertly done!
Luna was put under anaesthesia for the entirety of the procedure and received appropriate home care.
Check out our Facebook post for Luna’s Before and After reveal 11 days post-procedure: https://www.facebook.com/KimberleyVeterinaryClinic/post/pfbid033eGhUiwixarf2iGiJEhQ8urg6B1vBGk2jUYpFEXWfwA7YG6LrhZZDZYfuwTMQqahl
We do not condone or promote tattooing of animals for cosmetic purposes. This procedure must be done by trained professionals and under direct veterinary supervision as anaesthesia and proper analgesia are required.
If you would like to know more about having your pets tattooed for medical reasons, please contact VanCustoms directly.
https://m.facebook.com/VanCustomstattoos?eav=Afasb-dpxrENYpptz3DWtQmD_VnoAUGzV0Q4F8ordvbgEGc5N_sF-e4KItRsoP5CDgk&paipv=0&_rdr
Research Papers/Articles:
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26018407/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2010.01068.x
- https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=&ved=2ahUKEwiXpvzW8YmDAxVmgf0HHf_ACDIQFnoECAgQAQ&url=https%3A%2F%2Fepub.uni-regensburg.de%2F23795%2F1%2FDissertation_Lehner_endg.pdf&usg=AOvVaw3crauSTz5DW-NFPnhdsHTX&opi=89978449
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0737080608004310